Andersen's pointer analysis
Andersen's pointer analysis is a flow-insensitive, context-insensitive, and field-sensitive pointer analysis algorithm. It is used in static program analysis to determine which pointers in a program may point to which memory locations.
Overview
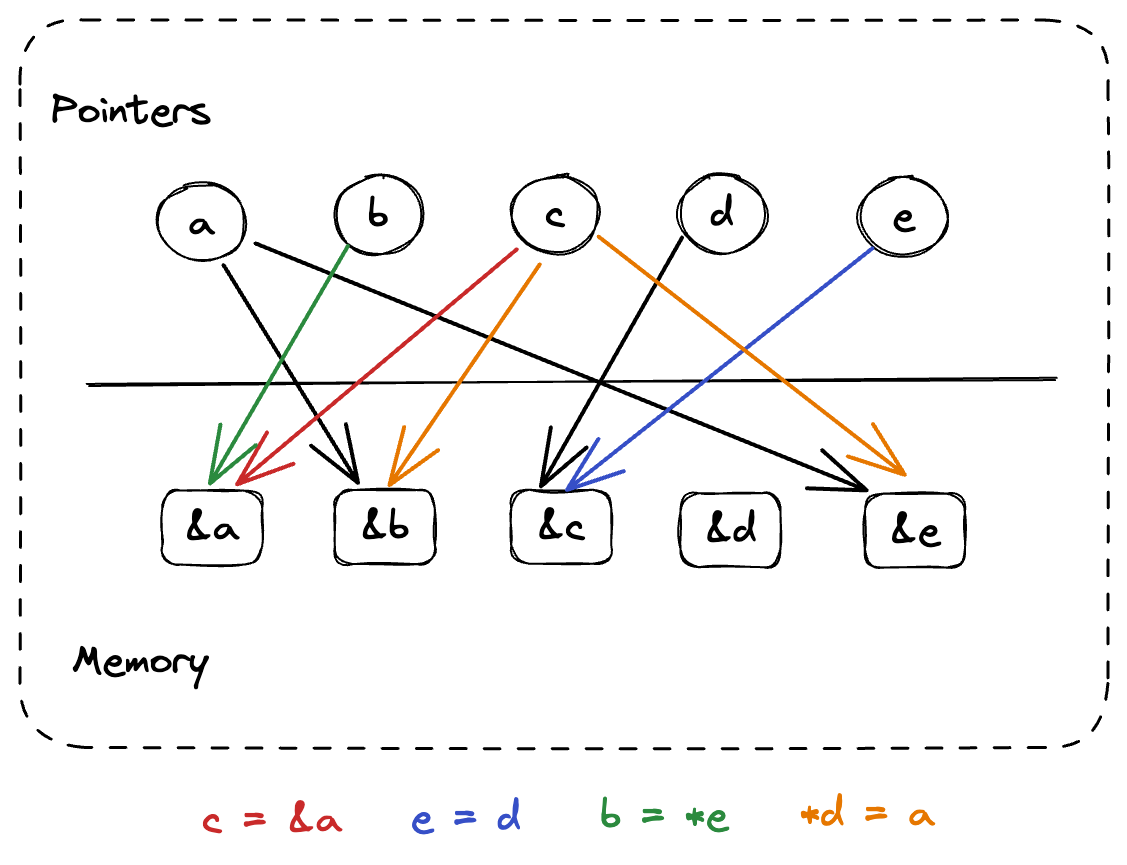
Andersen's analysis constructs a system of inclusion constraints on the points-to sets of pointers. These constraints are then solved to compute the possible memory locations each pointer may reference.
Key Characteristics
- Flow-Insensitive: Ignores program execution order; treats all statements as if they execute simultaneously.
- Context-Insensitive: Merges all function calls into a single analysis context.
- Field-Sensitive: Distinguishes between different fields in a structure (unlike field-insensitive analysis, which merges them).
Inclusion Constraints
| Statement | Inclusion Constraint |
|---|---|
a = b | PointsToSet(b) ⊆ PointsToSet(a) |
a = &b | b ∈ PointsToSet(a) |
a = *b | ∀c ∈ PointsToSet(b): PointsToSet(c) ⊆ PointsToSet(a) |
*a = b | ∀c ∈ PointsToSet(a): PointsToSet(b) ⊆ PointsToSet(c) |
Input and Output
Inputs:
A- a set ofnpointersS- a set ofmpointer-related statements.
Output:
- Exhaustive analysis - computes
PointsToSet(a)for all pointersa ∈ A. - On-demand analysis - Determines whether a specific
b ∈ PointsToSet(a)for given pointersa, b ∈ A.
Further Reading
[POPL 2021] The Fine-Grained and Parallel Complexity of Andersen's Pointer Analysis